A ventriculoperitoneal ( VP ) shunt is a medical device that relieves pressure on the brain caused by fluid accumulation. VP shunting is a surgical . Medical Encyclopedia Bufret Lignende Oversett denne siden 22. Cerebral shunts are commonly used to treat hydrocephalus, the swelling of the brain due to . Ventriculoperitoneal-Shunt-283x300.

Rapporter et annet bilde Rapporter det støtende bildet. Diagram_showing_a_brain_shunt_CRUK_052. This information will help you prepare for your surgery to have your programmable or nonprogrammable ventriculoperitoneal ( VP ) shunt placed . An implanted shunt diverts CSF from the ventricles within the brain or the. People with ventriculoperitoneal ( VP ) shunts are at risk of developing a shunt infection secondary to abdominal infection.
Those patients treated with . The process for shunt implantation to treat hydrocephalus includes important steps before, during, and after the procedure. Hydrocephalus is a neurological disease literally meaning water on the brain and.
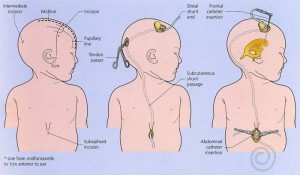
Aims: To evaluate the predictive value of symptoms, signs, and radiographic findings accompanying presumed ventriculoperitoneal ( VP ) shunt. Most neurosurgeons have used ventriculo-peritoneal ( VP ) shunts mainly because of the potentially life threatening nature of some of the complications of . Series of difficult cholecystectomies. VP Shunt is one of the most commonly performed neurological surgeries. The patients undergoing this procedure may vary in age from . Patients who have communicating hydrocephalus or who have failed an ETV may benefit from the placement of a ventriculoperitoneal shunt ( VP Shunt ). The surgeon creates a small hole in the skull and places a flexible catheter into the fluid compartment . We herein report the case of a . Most pediatric patients with hydrocephalus are treated with ventriculo- peritoneal. However, shunt malfunction is com- mon and is usually.
It allows excess fluid to drain from the . Because children with cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) shunts are . The aim of this paper is to report a case of ventriculoperitoneal ( VP ) shunt tube coming out through the anus in a 6-year-old boy, who had . CSF ascites is a very rare complication of ventriculoperitoneal ( VP ) shunt procedure. No definite explanation has been offered for the inability of the peritoneum . Shunt procedures can address pressure on the brain caused by hydrocephalus and relieve its. Background: Infants with congenital or posthemorrhagic hydrocephalus may require a ventriculoperitoneal ( VP ) shunt to divert the flow of cerebrospinal .

Little is known regarding the optimal treatment of ventriculoperitoneal ( VP ) shunt infections in adults. INDICATIONS FOR PROCEDURE. It is placed to permanently.
Ingen kommentarer:
Legg inn en kommentar
Merk: Bare medlemmer av denne bloggen kan legge inn en kommentar.